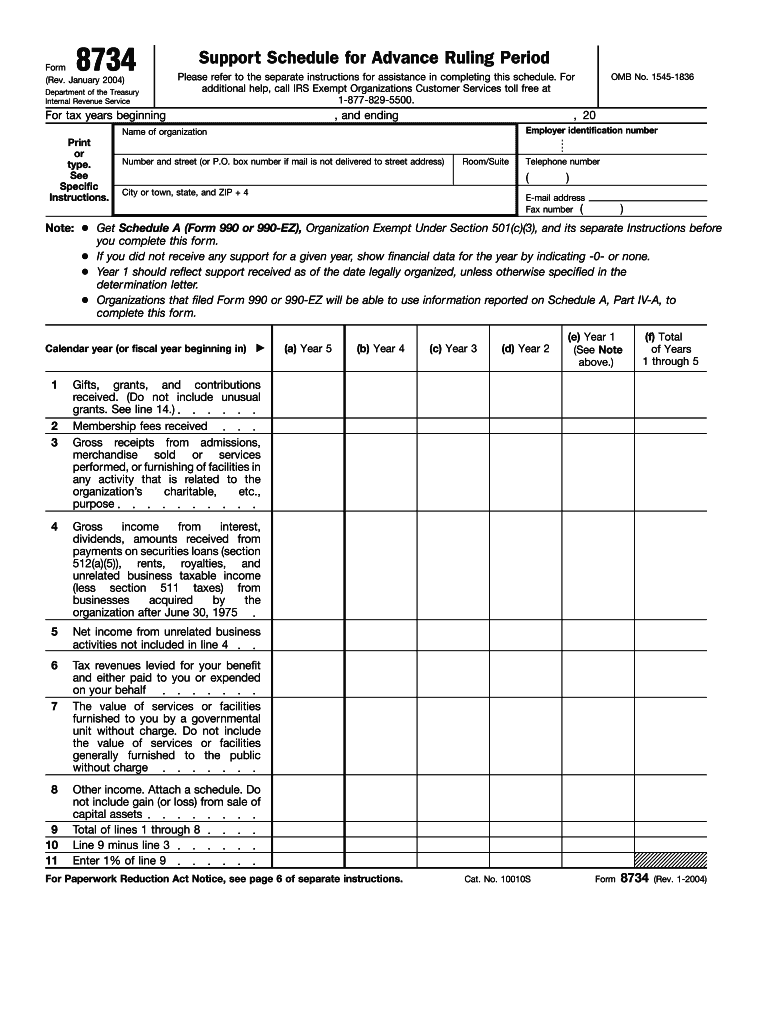
IRS 8734 2004-2025 free printable template
Get, Create, Make and Sign 990 purpose form

Editing 8734 pdf online
How to fill out din 6325 pdf form
How to fill out IRS 8734
Who needs IRS 8734?
Video instructions and help with filling out and completing form 990
Instructions and Help about din 6325 dowel pin
In this video I'm going to go through the fastest way to do the IRS form w-4 for 2021. Now this is the most updated IRS form w-4, so this is the one that you want to complete if you're filling out the iris form w-4 for 2021 now this method is not going to work for every situation but don't worry I have a ton of other videos on the IRS forum w4, and I'll continue to do more videos on the different variations and different versions of all the questions that you have with the IRS forum w4 now take a minute go into the comments let me know what your filing status is whether it's single married filing jointly head of household and if there are any situations that you have a question on or want to know a little more about on how to correctly fill out the IRS form w4 for 2021 now before we get into it if this is your first time at our channel, or you haven't subscribed click on the subscribe button at the bottom my name is Travis sickle certified financial planner helping you reach your financial goals now...
For pdfFiller’s FAQs
Below is a list of the most common customer questions. If you can’t find an answer to your question, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
How can I send ruling period for eSignature?
How do I edit form 8734 fill out on an iOS device?
How do I edit din 6325 hole tolerance on an Android device?
What is IRS 8734?
Who is required to file IRS 8734?
How to fill out IRS 8734?
What is the purpose of IRS 8734?
What information must be reported on IRS 8734?
pdfFiller is an end-to-end solution for managing, creating, and editing documents and forms in the cloud. Save time and hassle by preparing your tax forms online.